
Ensuring Cyber Trustworthiness: Key Role of Internal Audit in Your Business
Cyberattacks are increasing threats to businesses in today’s interconnected and digital world. Sensitive Data, Financial Assets, and the rest of the overall company’s reputation are at significant risk of Cyber-attacks. As technology plays a crucial role in daily operations; thus companies must take proactive measures toward cyber-trustworthiness. In 2023, the global average cost of data breaches was 4.45 million, a 15% increase over the last three years. In this blog, we will explore the critical role of Internal audit and its effectiveness in cyber risk management and cyber threats.
Understanding Internal Audit:
With the rise of cybersecurity threats, internal audit has expanded to include cyber risk management. Internal audit also has been associated traditionally with financial and compliance-related functions. Whether it be internal controls or governance processes, it plays a crucial role in enhancing and evaluating the effectiveness of risk management. To improve an organization’s operations, an Internal audit adds value as an independent & and objective assurance ally.
Expanding Landscape of Cybersecurity Threats:
Hackers and cybercriminals have become more sophisticated in their methods. Businesses face challenges in protecting themselves adequately from ransomware attacks, phishing attempts, data breaches, and insider threats. Regardless of the size of the business, businesses must be prepared to fight against these threats and maintain the trust of their customers and stakeholders.
Key Cyber Security Threats

The threat landscape has evolved with increasing reliance on technology and data-based operations. Cyber security threats have posed challenges to maintaining integrity, confidentiality, and sensitive information availability. Here are some key cyber security threats:
- Phishing: Phishing attack continues to be a pervasive threat that can exploit the psychology of humans. Phishing deceives individuals into revealing sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Ransomware attacks have grown in frequency, targeting businesses. Ransomware maliciously encrypts critical data and renders it accessible until it’s paid.
- Insider threats: Insider threats involve employees or other associated people of an organization who misuse internal access to compromised systems.
- Malware: Malware is an infiltrating system that steals sensitive data and establishes unauthorized access.
- Zero-day vulnerability: Zero-day vulnerability means flaws in software exploited by cybercriminals even before the vendor releases a patch for it.
- Data breaches and privacy concerns: Data breaches and privacy concerns can result in financial loss and erode customers’ trust in the company.
- Lack of cybersecurity awareness: Lack of cybersecurity awareness among the company employees and other stakeholders can amplify cyber threats.
Three Lines Model: Role and Responsibility
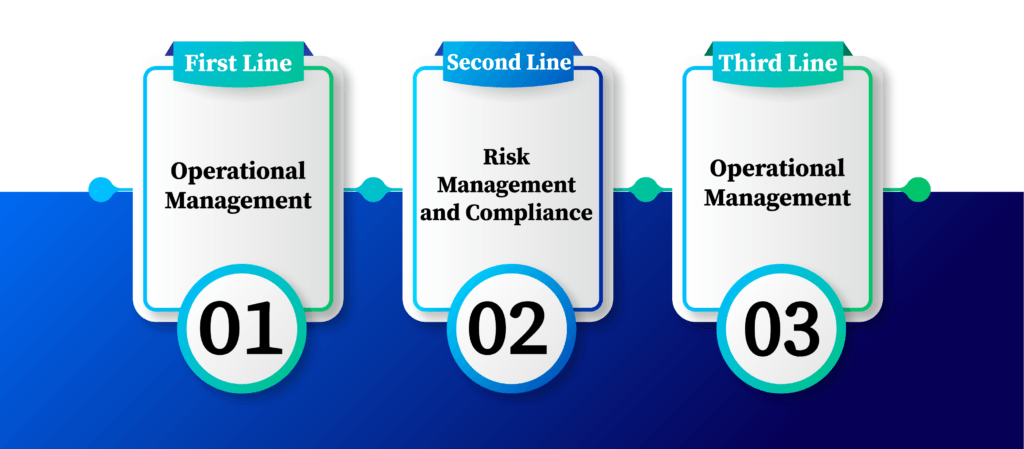
The lines model is an approach to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of risk and control functions within a company. It is provided by the Institute of Internal Auditors Three Lines Model.
The lines model is a framework that clarifies the roles and responsibilities of various risk management and control functions within a company. The Three Lines Model refers to as follows:
First line: Operational management
The first line comprises operational management responsibility for daily activities and processes. The key responsibilities are identifying and assessing cyber threats related to business. And then implementing cybersecurity measures, ensuring cybersecurity compliance, and cybersecurity training.
Second line: Risk management and compliance
The second line comprises risk management and compliance for overseeing and supporting the operations of the business. The second line establishes policies, frameworks, and procedures for risk control and management. Developing and conducting risk assessments and management, guidance, and support must be provided for cybersecurity measures and compliance.
Third line: Internal audit
The third line comprises internal audit functions that assure risk management effectiveness, process governance, and internal auditing. Verifying the accuracy and reliability of cyber-related information and collaborating with the first and second lines are the responsibility of the third line.
The Role of Internal Audit in Cyber Risk Management:

To safeguard their digital assets, organizations would need a robust cyber risk management strategy from growing cyber threats Outspread. Here are some Internal audit steps toward a pivotal role in the following ways:
Risk Assessment & Vulnerability Identification:
Teams of IT and Cybersecurity work closely with Internal Auditors. Risk assessment helps to assess potential risks & and identify their vulnerabilities in the organization. The organization’s network infrastructure, software applications, and data management processes are helped by the risk assessment process. Working together, this proactive approach allows businesses to detect and alleviate potential threats before they escalate into serious security breaches.
Compliance and Governance:
Despite maximum efforts, cyber incidents can still occur, and to ensure that the organization can quickly and effectively respond and recover from cyber incidents. The internal audit plays a vital role in establishing and testing incident response strategies. This proactive practice minimizes the potential damage and helps in business continuity.
Cybersecurity Awareness and Training:
For facilitating a strong cybersecurity culture within the organization, a good internal audit is crucial. Well-trained and vigilant employees act as an essential line of defense against cyber attacks. Hence, Internal audit helps to design and deliver cybersecurity training programs to employees, providing them with knowledge and responding to potential threats.
Third-party Risk Management:
Third-party vendors, suppliers, and partners often collaborate with companies in today’s interconnected environment. An Internal audit ensures they meet the organization’s security standards to assess the cybersecurity practices of these third parties. This does not pose a risk to the company’s operations and data.
Key Steps to Enhance Internal Audits Role in Cybersecurity
Here are the key steps for enhancing internal audits’ role in cybersecurity:
Utilization of technology:
Whether it’s about analyzing data, identifying vulnerabilities, or monitoring cyber threats, internal auditors should leverage technology tools and platforms.
Continuous Skill Development:
Internal auditors must continuously train to stay updated on the latest threats and technologies. This helps to perform best practices as cybersecurity is rapidly evolving. This results in providing adequate and relevant Suggestions to organizations.
Integration of Cybersecurity into the Audit Plan:
To ensure cybersecurity assessments are not conducted reactively and instead consistently and proactively, Internal Audit should include cybersecurity as a regular part of its audit plan.
Components of enterprise cyber preparedness
Here are the key steps for enhancing internal audits’ role in cybersecurity:
- Risk assessment: Businesses must plan and conduct regular risk assessments to identify and prioritize associated cyber risks.
- Security controls: Businesses need to implement appropriate security controls to protect their systems from any cyber threats.
- Continuous monitoring and improvement: Every business must regularly monitor its stance on cybersecurity and assess the effectiveness of its policies, procedures, and controls.
- Governance: Governance states that businesses must have cybersecurity governance policies, frameworks, and procedures.
Collaboration with IT and Cybersecurity teams
When IT, Cybersecurity, and internal audit teams work together, they manage cyber risks well. This teamwork also helps them learn about the company’s technology, tools, and safety practices. Internal audits can use the knowledge of IT and Cybersecurity experts to create good ways to check for risks.
The Future of Internal Audit and Cybersecurity

Internal audit’s role in Cybersecurity is becoming more critical as cyber threats evolve. Artificial intelligence and machine learning-powered threat detection systems are the skills to understand the latest cybersecurity tools and techniques. Internal audit professionals are required to update these skills continuously. To stay abreast of emerging cybersecurity trends, technologies, and regulatory changes. This helps to evaluate and address cyber risks efficiently.
End note:
Cyber incidents are considered the greatest risk faced by businesses worldwide. Internal Audit emerges as a stalwart guardian for any business’s cyber trustworthiness in the age where cyber threats are so tending. A robust internal audit is important for various aspects like risk assessment, compliance, control evaluation, employee education, and incident response. Internal audits play a vital role in preparing businesses to navigate the intricate realm of cyber risks. They achieve this by working closely with IT and Cybersecurity teams.
Contact us to get free consultation related to internal audits.
